How to use High Cholesterol products for health improvement.
Introduction: Understanding Cholesterol and Its Role in Health
Cholesterol is a vital substance found in every cell of the human body. It plays an essential role in maintaining the structure of cell membranes and is involved in the production of critical hormones such as estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol, as well as vitamin D and bile acids for fat digestion. Despite its importance, when cholesterol levels in the blood become too high, particularly LDL cholesterol (Low-Density Lipoprotein), it can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease, strokes, and arterial blockages.
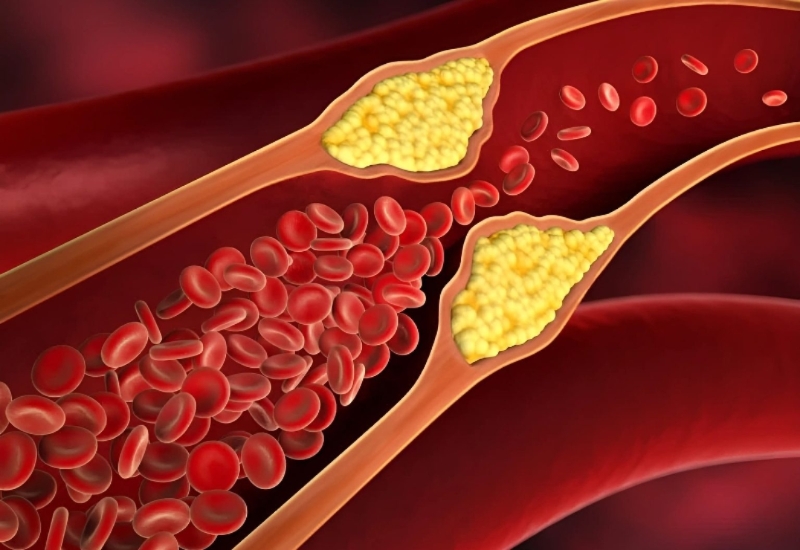
Not all cholesterol is harmful, however. HDL cholesterol (High-Density Lipoprotein), often referred to as “good cholesterol,” helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream, protecting the arteries from plaque buildup.
This article will explore how high-cholesterol products, specifically those containing oxidized cholesterol, can be used for health improvement. We will examine the science behind oxidized cholesterol, its potential benefits and risks, and how these products can be incorporated into a healthy lifestyle.
Cholesterol: The Good, the Bad, and the Misunderstood
LDL Cholesterol (Bad Cholesterol)
LDL cholesterol is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol because it can accumulate in the walls of blood vessels and form plaques (atherosclerosis), which can block blood flow and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes. However, not all LDL cholesterol is harmful. Recent studies suggest that not all LDL particles are equally dangerous. Small, dense LDL particles are more likely to stick to artery walls and cause damage, while larger, more buoyant LDL particles are less likely to cause issues. Thus, lowering LDL cholesterol to the lowest possible level may not always be the best approach for everyone.
HDL Cholesterol (Good Cholesterol)
HDL cholesterol is called “good” cholesterol because it helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and transport it back to the liver, where it is processed and eliminated. Maintaining high levels of HDL cholesterol is crucial for cardiovascular protection. Foods rich in unsaturated fats, such as olive oil, chia seeds, and fatty fish, can help increase HDL levels in the body.
Oxidized Cholesterol (The Hidden Danger)
Oxidized cholesterol forms when cholesterol, particularly LDL cholesterol, reacts with free radicals in the body, undergoing a process known as oxidation. This results in molecules of oxidized cholesterol, which can be harmful. Oxidized cholesterol is thought to promote inflammation in the arteries, leading to plaque formation and contributing to cardiovascular disease. While oxidized cholesterol is often associated with negative health outcomes, recent research suggests that it might have beneficial effects in certain contexts, such as reducing inflammation and supporting cardiovascular health when used appropriately.
What is Oxidized Cholesterol?
The Science of Oxidation
Oxidized cholesterol is formed when cholesterol, particularly LDL, reacts with reactive oxygen species (ROS) or free radicals in the body. This oxidation process alters the chemical structure of the cholesterol molecule, making it more prone to causing damage within the body. Oxidized cholesterol is considered a major contributor to the development of cardiovascular diseases because it can lead to the formation of plaques in the arteries, which restrict blood flow and increase the risk of heart disease.
Interestingly, some studies suggest that oxidized cholesterol may have certain health benefits when used properly. For example, it may have anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce inflammation in the arteries and improve overall cardiovascular health.
How Oxidized Cholesterol Affects Health
The oxidation of cholesterol in the bloodstream has been linked to the development of atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in the arteries). This is because oxidized cholesterol triggers an immune response, causing inflammation in the artery walls. Chronic inflammation can lead to the hardening and narrowing of arteries, which increases the likelihood of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular issues.
However, some experts believe that oxidized cholesterol may have therapeutic
How Oxidized Cholesterol Products Work
The Benefits and Risks
Products containing oxidized cholesterol are marketed for their potential health benefits, particularly in reducing inflammation and supporting cardiovascular health. Some studies suggest that oxidized cholesterol may help improve blood vessel function, decrease inflammation, and even reduce the risk of heart disease by promoting healthy cholesterol metabolism.
However, there are risks associated with consuming too much oxidized cholesterol. Overconsumption can lead to excessive plaque buildup in the arteries, which might negate any potential benefits. Therefore, it is essential to understand the balance between therapeutic use and overuse of these products.
Therapeutic Uses
Some studies have shown that oxidized cholesterol can support the reduction of inflammatory markers in the body. Inflammation is a major contributor to various chronic diseases, particularly heart disease. Oxidized cholesterol products, when used in moderation and under proper supervision, may have a role in reducing these markers and promoting better cardiovascular health.
On the other hand, excessive exposure to oxidized cholesterol can worsen health problems, such as increasing the risk of arterial damage and exacerbating cardiovascular issues.
Using High Cholesterol Products for Health Improvement
Safe Use Guidelines
To safely incorporate high cholesterol products, especially those containing oxidized cholesterol, into your diet, it’s essential to follow specific guidelines. One of the primary considerations is ensuring that the cholesterol consumed is balanced with other nutrients. A diet rich in healthy fats, antioxidants, and fiber can help mitigate the potential risks of consuming high levels of cholesterol.
When using high cholesterol products, such as supplements or fortified foods, it’s important to work with a healthcare provider to monitor cholesterol levels regularly. Regular blood tests can help assess the effects of these products on your lipid profile and overall health.
Supplementation vs. Natural Intake
While some people may choose to use supplements containing high cholesterol or oxidized cholesterol, others may prefer to obtain cholesterol through natural food sources. Foods that naturally contain cholesterol, such as eggs, dairy products, and certain meats, can be included in a balanced diet. However, it’s important to consume these foods in moderation to avoid exceeding recommended cholesterol intake levels.
Health Improvement Strategies
Incorporating high cholesterol products for health improvement should be done alongside a healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity, stress management, and weight control. Studies have shown that exercise can help improve HDL cholesterol levels, while reducing the impact of LDL cholesterol on arterial health. Additionally, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is crucial for supporting overall heart health.
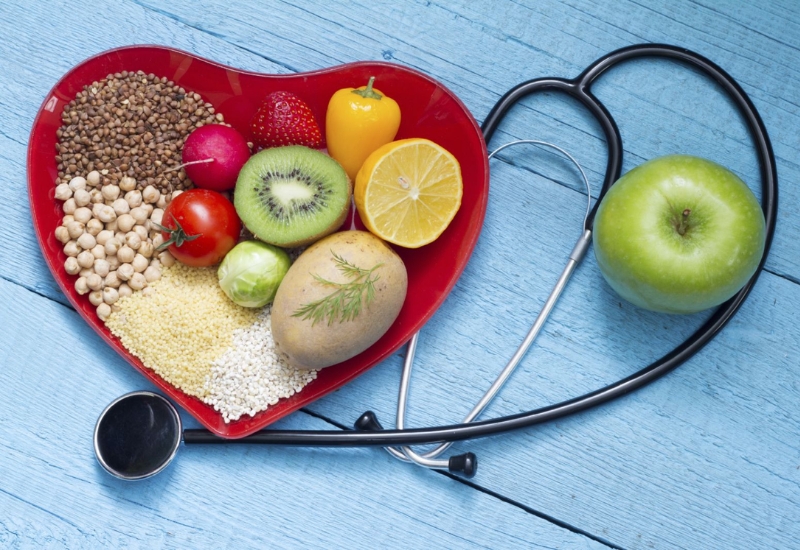

Role of Diet in Cholesterol Management
Foods to Increase Good Cholesterol (HDL)
To promote healthy cholesterol levels, it’s important to consume foods that help increase HDL cholesterol. These include:
- Healthy fats: Olive oil, avocado, and nuts are excellent sources of unsaturated fats that can help boost HDL levels.
- Fatty fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which are known to increase HDL cholesterol.
- Whole grains: Foods like oats, barley, and quinoa can help raise HDL levels while providing essential fiber for digestive health.
Foods to Lower Bad Cholesterol (LDL)
To lower LDL cholesterol, focus on consuming foods that help reduce bad cholesterol, such as:
- Fruits and vegetables: These are rich in antioxidants and fiber, which help reduce LDL cholesterol levels.
- Legumes and beans: These are excellent plant-based sources of protein that can lower LDL cholesterol.
- Soluble fiber: Foods like oats, beans, and psyllium husk are rich in soluble fiber, which helps reduce cholesterol absorption.
Importance of Antioxidants
Antioxidants play a crucial role in neutralizing free radicals and preventing the oxidation of cholesterol. Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, dark leafy greens, and nuts, can help protect the body from oxidative stress and reduce the harmful effects of oxidized cholesterol.
Conclusion

High cholesterol products, particularly those containing oxidized cholesterol, have potential health benefits but also come with risks. By understanding the science behind cholesterol, the role of oxidized cholesterol in health, and how to use these products safely, individuals can make informed choices about their health. It is important to balance the use of high cholesterol products with a healthy diet and lifestyle, including regular exercise, stress management, and weight control, to ensure optimal cardiovascular health.








